Structure, Functions, and Common Issues
Introduction The lower back, also known as the lumbar region, plays a vital role in your body's overall functionality and movement. Whether you are an athlete, an office worker, or anyone in between, the health of your lower back is crucial for your daily activities. In this blog we explore the anatomy of the lower back, its functions, common problems that can arise, and general care tips to maintain a healthy spine.
Anatomy of the Lower Back
The lower back is composed of five vertebral bones, known as L1 through L5. These vertebrae are larger than those in the thoracic and cervical spine regions, as they bear the most weight and are subjected to the greatest mechanical stress. Between these vertebrae are intervertebral discs, which act as cushions and shock absorbers, allowing for flexibility and providing protection against impact.
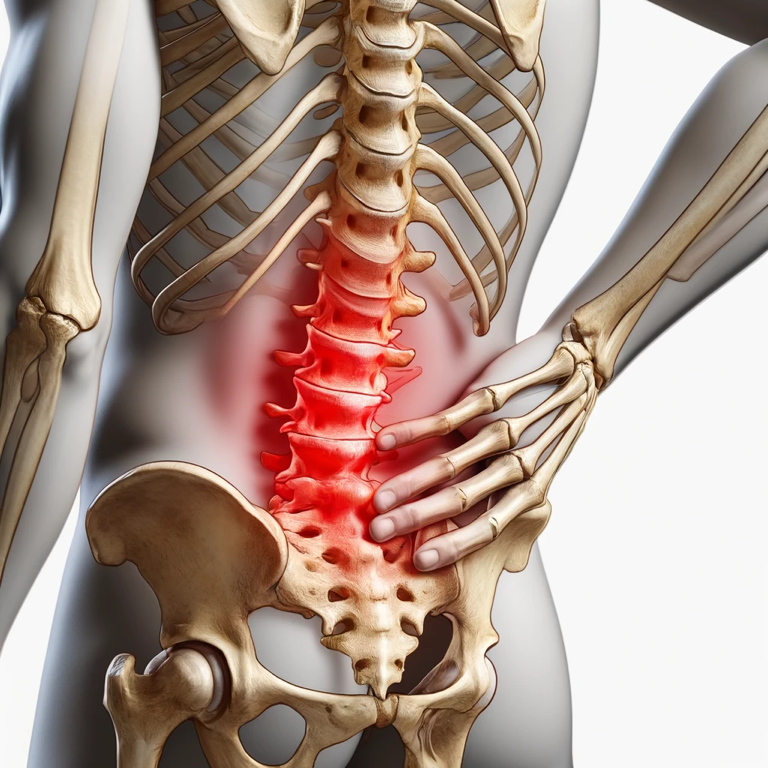
Supporting the vertebrae and discs are various muscles and ligaments that help stabilise the spine and allow for movements such as twisting and bending. The major muscles include the erector spinae, which help maintain upright posture, and the multifidus and quadratus lumborum, which support spinal alignment and facilitate movement.
Functions of the Lower Back
The primary function of the lower back is to provide structural support, movement, and protection of certain body tissues. The lumbar spine holds up the weight of the torso, providing a center of gravity when you move, which is essential for balance and mobility. It also houses and protects the spinal cord and nerves that connect the brain to the rest of the body, enabling sensory and motor function.
Common Lower Back Problems
Lower back pain is one of the most common health complaints globally, affecting millions of people each year. Here are a few prevalent issues:
1. Muscle or Ligament Strain:
Repeated heavy lifting or a sudden awkward movement can strain back muscles and spinal ligaments.
2. Bulging or Ruptured Discs:
The discs can bulge or rupture and press on a nerve, causing pain that can be severe.
3.Sciatica:
A sharp, shooting pain that travels through the buttock and down the back of the leg, caused by a bulging or herniated disc pressing on a nerve.
4. Arthritis:
Osteoarthritis can affect the lower back, sometimes leading to narrowing of the space around the spinal cord (spinal stenosis).
5. Skeletal Irregularities:
Conditions like scoliosis, a curvature of the spine, can lead to back pain later in life. Preventing and Managing Lower Back Problems Maintaining a healthy lower back involves a combination of preventive measures and appropriate responses to emerging pain.
Here are some tips:
Exercise Regularly
Core strengthening exercises can stabilise your spine, and flexibility training can enhance your back’s range of motion.
Proper Posture
Learning and maintaining proper posture while sitting, standing, and lifting can prevent excessive strain on your lower back.
Ergonomic Adjustments
Ensure your workspace supports your back. Chairs with proper lumbar support and desks at the correct height can reduce strain.
Manage Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the load on your spine, decreasing the chances of developing back issues.
Professional Help
If you experience persistent back pain, consulting a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and a treatment as an exercise plan is crucial.
Conclusion
Understanding the anatomy and functionality of your lower back is the first step towards effectively managing its health. By incorporating preventive care and addressing any issues promptly, you can maintain a strong and healthy back, facilitating an active and pain-free lifestyle. Remember, your back supports you in every physical activity you undertake, so it's essential to take good care of it.



Contact Us.
Fuelling Clinics' Growth, Empowering Vibrant Health.
Thank you for exploring our innovative approach to bone health. As a potential partner, your commitment to expanding care and services at your clinic inspires us.
By integrating our technology, you can transform countless lives, helping your patients improve their bone health, enhance their strength, and regain their balance.
Contact Us
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.
Performance Health Systems MSK
